You are here: GSI Wiki>Linux Web>SslCertificates (2013-12-03, ChristopherHuhn)Edit Attach
SSL certificates
Many services at GSI are only available via SSL encrypted communication (i.e.https://..., Mailbox access, ...). The server certificates (keys) for these encrypted communication channels are issued and signed by the DFN.
The SSL certificates are all signed by this certificate chain: - https://www.pki.dfn.de/fileadmin/PKI/zertifikate/deutsche-telekom-root-ca-2.crt Deutsche Telekom Root CA 2 (SHA-1 fingerprint
85:A4:08:C0:9C:19:3E:5D:51:58:7D:CD:D6:13:30:FD:8C:DE:37:BF) - GSI CA 02 (SHA-1 fingerprint
2B:43:9C:97:05:16:3B:EA:1F:28:5F:57:94:DC:63:73:2D:77:A1:32)
Mozilla apps
Recent releases of the Mozilla suite applications Firefox (aka. Iceweasel), Thunderbird (aka. Icedove) and Seamonkey (aka. Iceape) trust DFN-signed certificates by default. For older versions you have to import the relevant certificates by yourself to make Firefox et al. trust GSI SSL certificates.Firefox
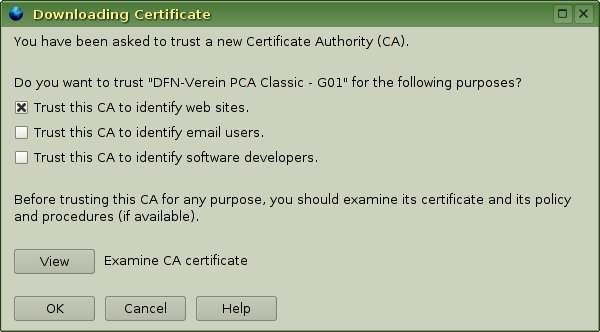 Simply click on the certificate links above. An https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/firefox_add_ca_sarge.png import dialog will appear. Choose at least Trust this CA to identify web sites and click ok. Adding trust for email users in Firefox is as useless as for software - currently there's no known software signed by a GSI certificate.
Simply click on the certificate links above. An https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/firefox_add_ca_sarge.png import dialog will appear. Choose at least Trust this CA to identify web sites and click ok. Adding trust for email users in Firefox is as useless as for software - currently there's no known software signed by a GSI certificate.
Thunderbird
 GSIs Exchange mail server also uses a DFN-signed SSL certificate for encrypting the IMAP and POP client access (see TipsEmail).
To make Thunderbird trust this certificate you have to download the certificates above on your local computer first.
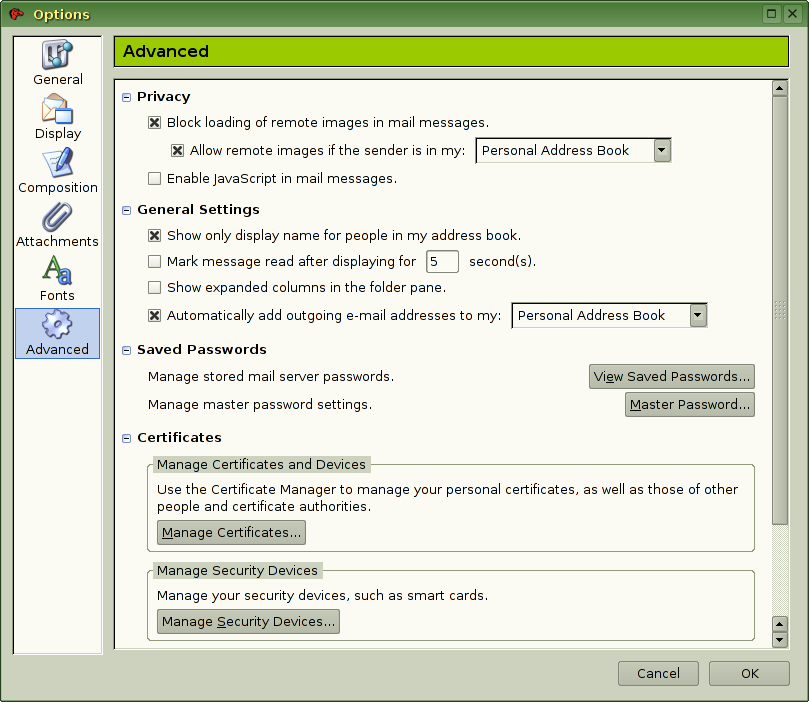
Then open Thunderbird's configuration dialog (Edit - Preferences) and go to the tab https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/thunderbird_preferences_advanced_sarge.png Advanced.
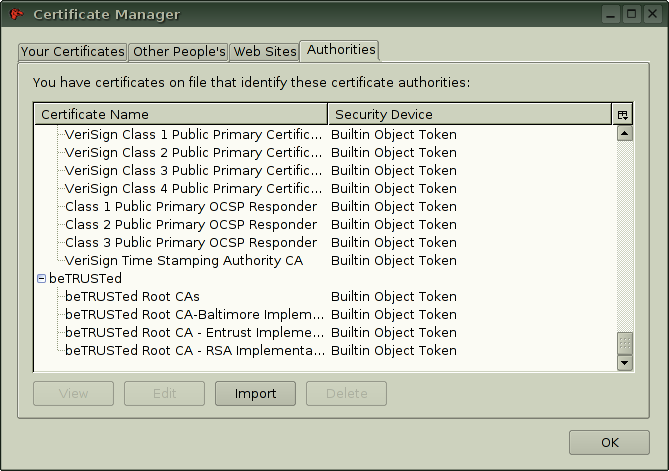
Click Manage certificates to open the https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/thunderbird_certificate_manager_sarge.png Certificate Manager, go to the tab Authorities and click Import to import the locally saved certificates.
Choose Trust this CA to identify web sites in the appearing https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/firefox_add_ca_sarge.png import dialog.
You may additionally choose Trust this CA to identify email users to make Thunderbird trust mails signed by S/MIME using DFN signed certificates (rarely used up to now).
GSIs Exchange mail server also uses a DFN-signed SSL certificate for encrypting the IMAP and POP client access (see TipsEmail).
To make Thunderbird trust this certificate you have to download the certificates above on your local computer first.
Then open Thunderbird's configuration dialog (Edit - Preferences) and go to the tab https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/thunderbird_preferences_advanced_sarge.png Advanced.
Click Manage certificates to open the https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/thunderbird_certificate_manager_sarge.png Certificate Manager, go to the tab Authorities and click Import to import the locally saved certificates.
Choose Trust this CA to identify web sites in the appearing https://wiki.gsi.de/pub/Linux/SslCertificates/firefox_add_ca_sarge.png import dialog.
You may additionally choose Trust this CA to identify email users to make Thunderbird trust mails signed by S/MIME using DFN signed certificates (rarely used up to now).
KDE
Yet to come ...OpenSSL applications
The majority of applications, especially cmdline programs likesvn or wget use the http://www.openssl.org/ OpenSSL library for SSL encryption (or GnuTLS for which these instructions also apply).
This has already been preconfigured throughout the GSI LinuxFarm, so the following instructions are only necessary on external computers. You need superuser privileges for installation.
The trusted root certificates for OpenSSL normally reside below /etc/ssl/certs/. Download the certificates and copy them to /etc/ssl/certs/. Then run c_rehash /etc/ssl/certs. That's it.
Alternative for Debian-based distros: - Download the certificates to /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
- Run
sudo update-ca-certificates
Edit | Attach | Print version | History: r8 < r7 < r6 < r5 | Backlinks | View wiki text | Edit wiki text | More topic actions
Topic revision: r8 - 2013-12-03, ChristopherHuhn
<!-- With LdapContrib WikiUsers becomes irrelevant -->
%IF{"'%WIKINAME%'!='WikiGuest'" then="$n * [[$percentUSERSWEB$percent.$percentWIKIUSERSTOPIC$percent][ $percentICON{\"person\"}$percent $percentMAKETEXT{\"Users\"}$percent]]"}% \
 Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding GSI Wiki? Send feedback | Legal notice | Privacy Policy (german)
